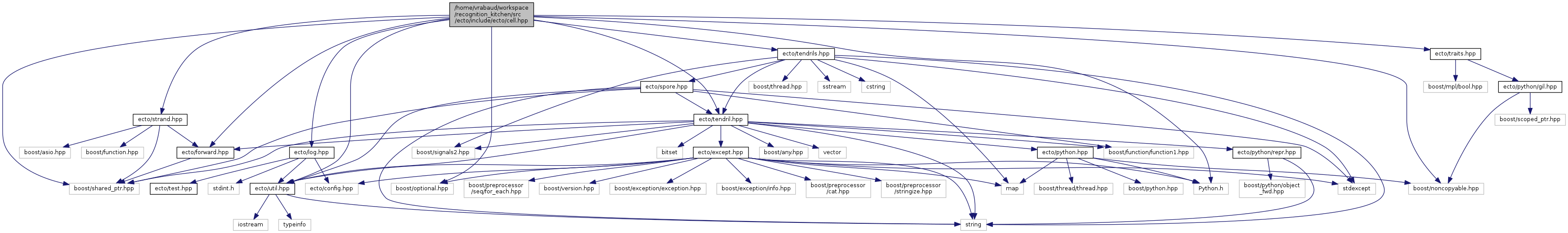
#include <Python.h>
#include <ecto/forward.hpp>
#include <ecto/log.hpp>
#include <ecto/strand.hpp>
#include <ecto/tendril.hpp>
#include <ecto/tendrils.hpp>
#include <ecto/traits.hpp>
#include <ecto/util.hpp>
#include <boost/noncopyable.hpp>
#include <boost/optional.hpp>
#include <boost/shared_ptr.hpp>
Go to the source code of this file.
|
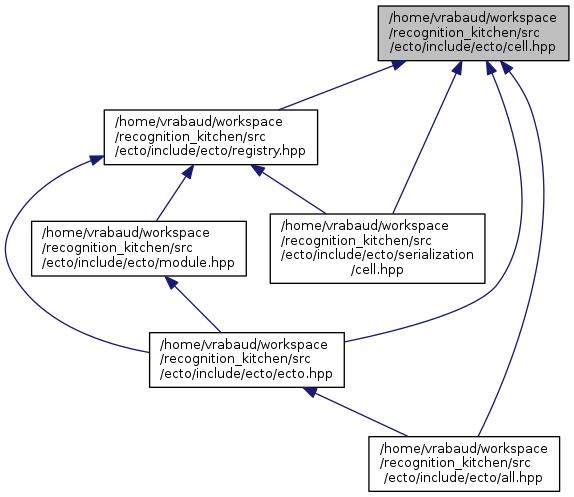
| struct | ecto::cell |
| | ecto::cell is the non virtual interface to the basic building block of ecto graphs. This interface should never be the parent of client cell, but may be used for polymorphic access to client cells. More...
|
| |
| struct | ecto::has_f< T > |
| | Helper class for determining if client modules have function implementations or not. More...
|
| |
| struct | ecto::cell_< Impl > |
| | cell_<T> is for registering an arbitrary class with the the cell NVI. This adds a barrier between client code and the cell. More...
|
| |
| struct | ecto::cell_< Impl >::int_< I > |
| |
| #define ECTO_RETURN_VALUES (OK)(QUIT)(DO_OVER)(BREAK)(CONTINUE)(UNKNOWN) \ |
 1.8.11
1.8.11